The digital landscape has dramatically shifted, with the AI era demanding a new SEO approach: topical authority. This comprehensive Webspero Solutions guide equips you with the strategies to master it, significantly improving your visibility, and become a trusted leader in your niche.
Key Takeaways
But before we dive deep, here’s a quick overview of what you’ll learn in this guide:
|
In 2021, the idea of topical authority began gaining traction within the SEO world as Google launched MUM (Multitask Unified Model)1. However, it wasn’t until 2025 that the concept truly took off, for the search engines continued to evolve and the challenges of ranking, gaining visibility, and securing clicks in search results kept growing higher.
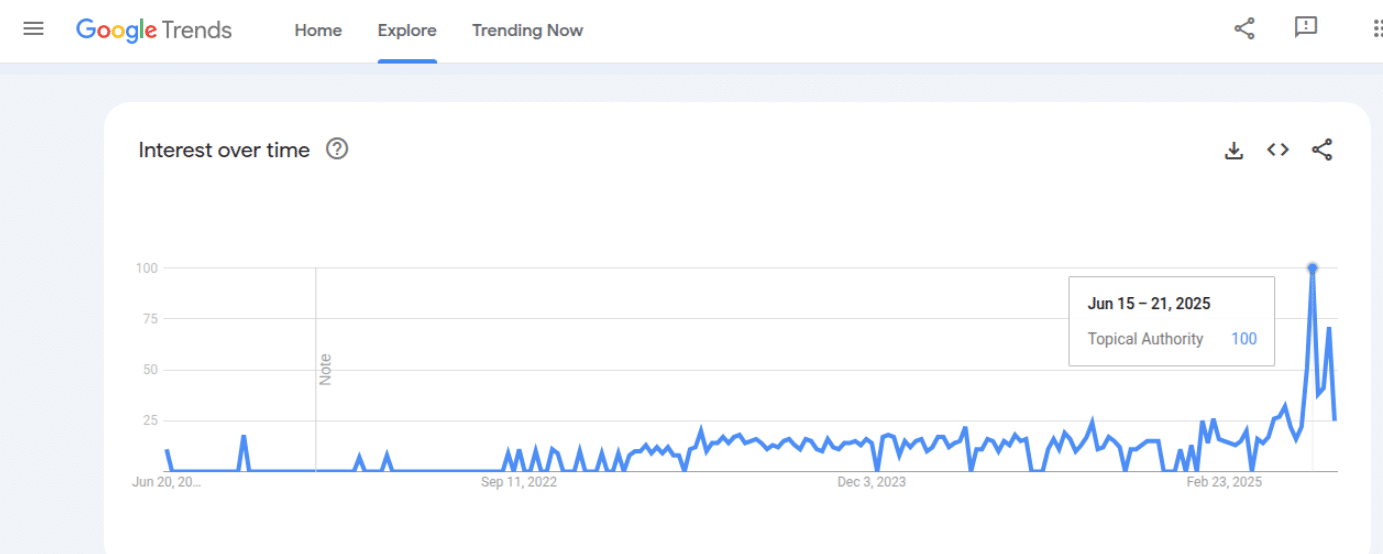
Why did this shift happen?
It’s because Search engines, in their earlier iterations, functioned more like matchmakers. They would look for keywords on your website and match them with the queries people were searching for. If your site had the right keywords, it would show up in search results.
However, with the rise of AI and smarter search algorithms, search engines have evolved into Answer Engines 2. They now provide direct answers to users right in the search results without the need for clicks—this shift is what we call Zero-Click SEO 3
In this new landscape, topical authority is what determines whether it’s your website that gets chosen to provide those direct answers to users.
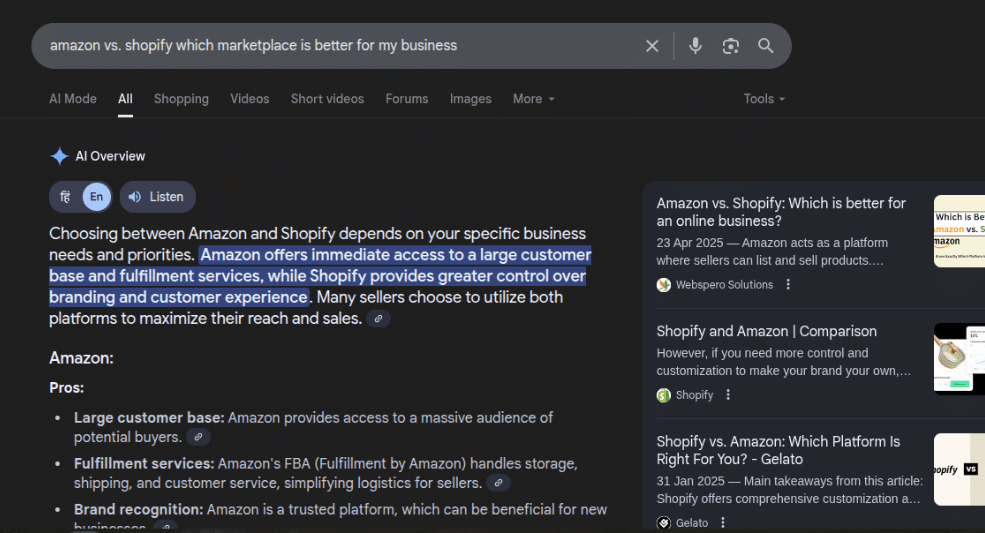
(Take our own comparison content on Amazon vs. Shopify. It often appears in AI Overviews, sometimes even above Shopify itself! This happens because we’ve built authority through original, research-backed comparisons that the algorithm trusts to provide accurate information.)
What is Topical Authority?
Topical authority means that both search engines (like Google) and your audience recognize your website as the most comprehensive and trustworthy source of information on a specific subject.
If Google sees that your website consistently produces high-quality, relevant, and comprehensive content on a particular topic, it will rank your site highly for related queries.
For example, imagine your website as that one friend who knows everything about bikes. Need advice on fixing a flat tire? Or looking for the best gear for a mountain trail? They’re your go-to source.
Just like you rely on that friend for expert advice, users should trust your website as the expert on a particular subject.
It should be noted that topical authority isn’t just about getting technical details right; it’s about earning your audience’s trust and becoming the go-to resource in your niche.
TL;DR: Topical authority is like earning the ultimate title of a subject matter expert for your website.
So, how does Google “recognize” this authority? It evaluates a combination of signals:
|
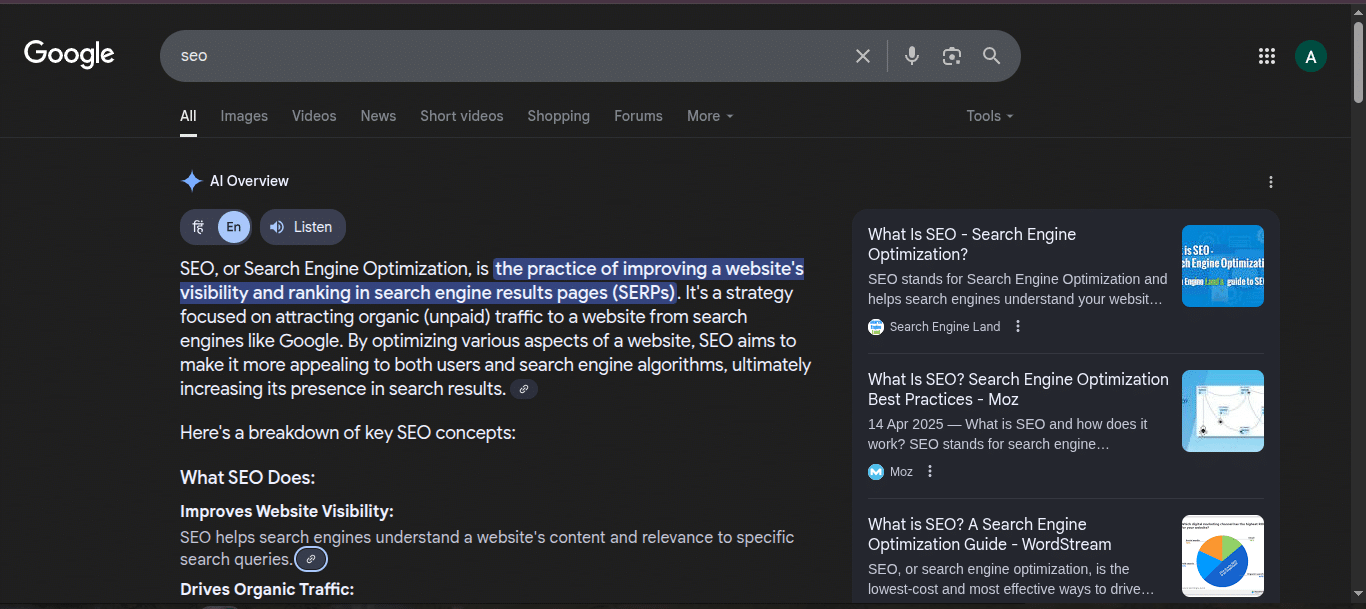
(As seen here, Moz and Search Engine Land, leading authorities in SEO, appear in the AI Overview for ‘What is SEO?’ due to their comprehensive, trusted, and in-depth content on SEO topics. With Moz having written 5000+ blogs, they’ve established themselves as a go-to source for SEO knowledge.)
Why Topical Authority Matters More Than Ever (Especially in the Age of AI)
Of all the things that your company owns, brands are far and away the most important and the toughest. Brand loyalty is the only sound foundation on which business leaders can build enduring, profitable growth.
This concept remains as relevant today as it was in the past; being recognised as a trusted source is key to long-term success in the digital world.
The undeniable importance of it stems from several key reasons:
1. Topical Authority Fuels AI Overviews (AIOs)
Search engines, like Google, now use Artificial Intelligence (AI) to provide direct answers to user queries in what’s known as AI Overviews or featured snippets.
If your site isn’t deeply authoritative, you’re invisible in these summaries, no matter how good your content is.
2. It Future-Proofs Your Rankings
Google’s ranking algorithm evolves over time, and this can cause fluctuations in rankings. However, sites that cover a topic comprehensively and maintain good internal linking are more stable and better positioned to maintain high rankings despite updates.
3. It Builds Trust with Users (and Converts Better)
When your website consistently provides high-quality and useful content, users begin to trust it as a reliable source. This trust is a powerful factor in increasing conversions, whether it’s sign-ups, purchases, or other desired actions.
Plus, users tend to stay longer on a site that answers multiple questions or provides a thorough resource. Lower bounce rates (users staying on your site longer) and higher engagement (subscribing, purchasing) are signs of trust and authority.
4. You Get More Organic Reach with Less Effort
Authoritative sites rank faster, even for newly published content, though success depends on competition and quality.
That’s because Google recognizes you as a credible expert and trusts you to provide accurate, helpful answers.
5. It Makes Every Other SEO Investment Worth More
Whether you’re spending on link-building, social promotion, or paid search, those efforts are amplified when they point to a site with strong topical authority. It multiplies ROI(Return on Investment).
6. It’s Your Moat in a Crowded Content Landscape
A moat is something that protects your business from competition.While anyone can publish content, only a few sites can dominate a specific niche or subject.
Becoming the best, most comprehensive source makes it difficult for competitors or AI to replace you.
TL;DR: Topical authority is how you rank now – and how you stay ranked tomorrow.
How to Build Topical Authority for AI Engines
Turning your website into a trusted resource isn’t about publishing one viral article and calling it a day. It’s a strategic, long-term commitment to earning a reputation over time.
And, you earn a reputation by trying to do hard things well.
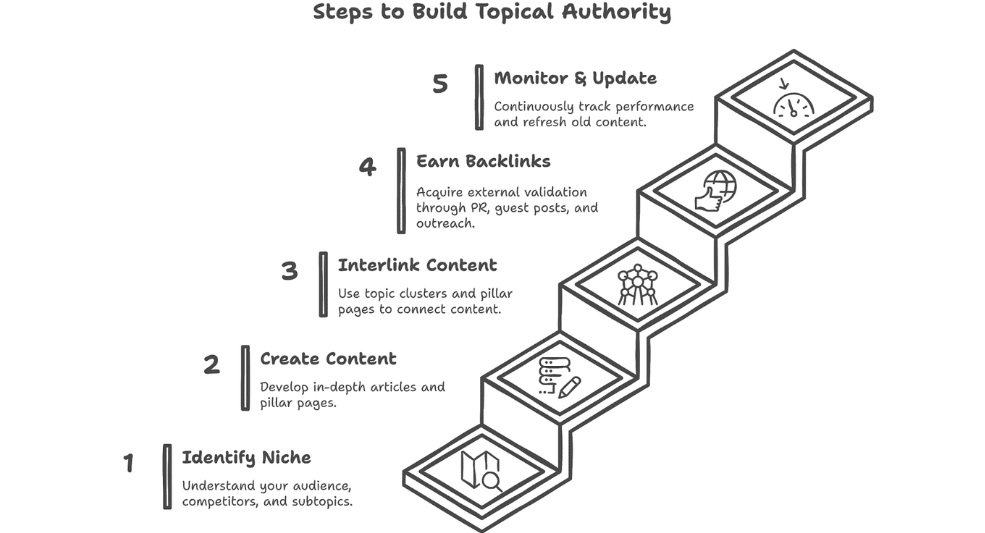
1. Cover the Topic Completely (Strategic Foundations)
To establish authority, you must explore every angle of your topic. Just a few articles won’t cut it. Think of building a comprehensive knowledge hub where everything related to the topic is easily accessible.
But before you even start writing, lay the groundwork: understand your niche, your audience, and your competitors. This research ensures your content is comprehensive and truly meets your audience’s needs.
1.1 Audience Persona Segmentation
- Build 3–4 personas: Define 3 or 4 distinct customer profiles that represent different segments of your target audience. These personas are based on real customer data and behavior, helping you better understand the specific needs, goals, and challenges of each segment.
- Define their goals: For each persona, identify their key goals; what they want to achieve when they visit your site. This helps you understand what they are looking for.
- Identify their challenges: Understand the obstacles or pain points each persona faces. Knowing these challenges helps you see what’s preventing them from achieving their goals.
- Create content that addresses their needs: With their goals and challenges in mind, develop content that directly addresses each persona’s issues, making your content more relevant and engaging.
Example Persona for a Shopify SEO Blog:
- Name: “Starter Sarah”
- Role: New Shopify Store Owner (0-6 months).
- Needs: Simple, non-technical SEO guides. She searches for terms like “how to add keywords to Shopify” and “easy SEO for my store.”
- Goals: Get her first organic sale. Avoids complex tools and jargon.
Understanding what type of content (e.g., guides, videos, blog posts) each persona prefers will also allow you to tailor your delivery method.
1.2 Keyword & Topic Universe Mapping
- Seed Brainstorm:
Start by brainstorming broad keywords that define your niche. These are general terms that will guide your content creation and keyword research. (e.g., “Shopify SEO,” “site speed Shopify,” “product image optimization”).
- Map Out Topics and Keywords:
Identify the main topics and keywords that define your subject. Understand the user intent behind each search query to ensure your content matches what users are looking for.
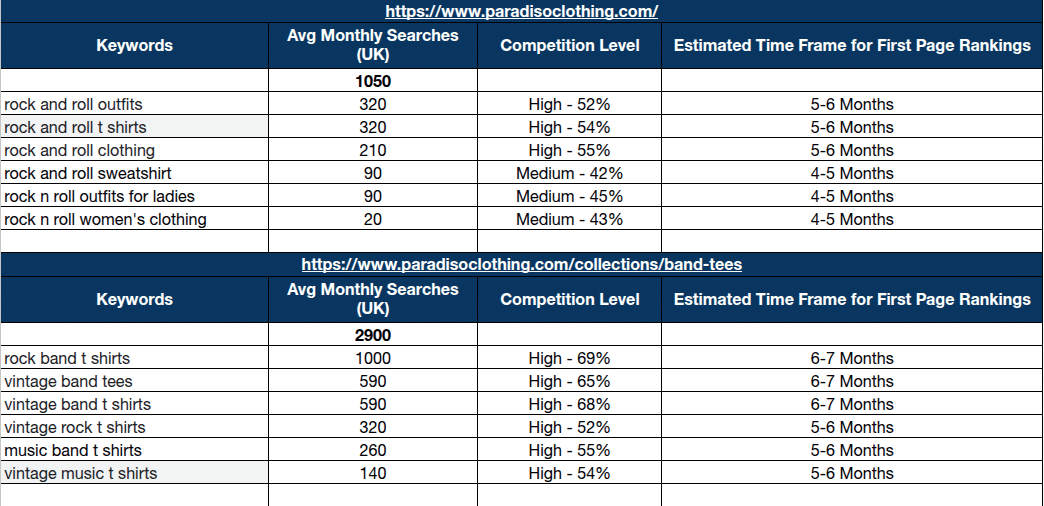
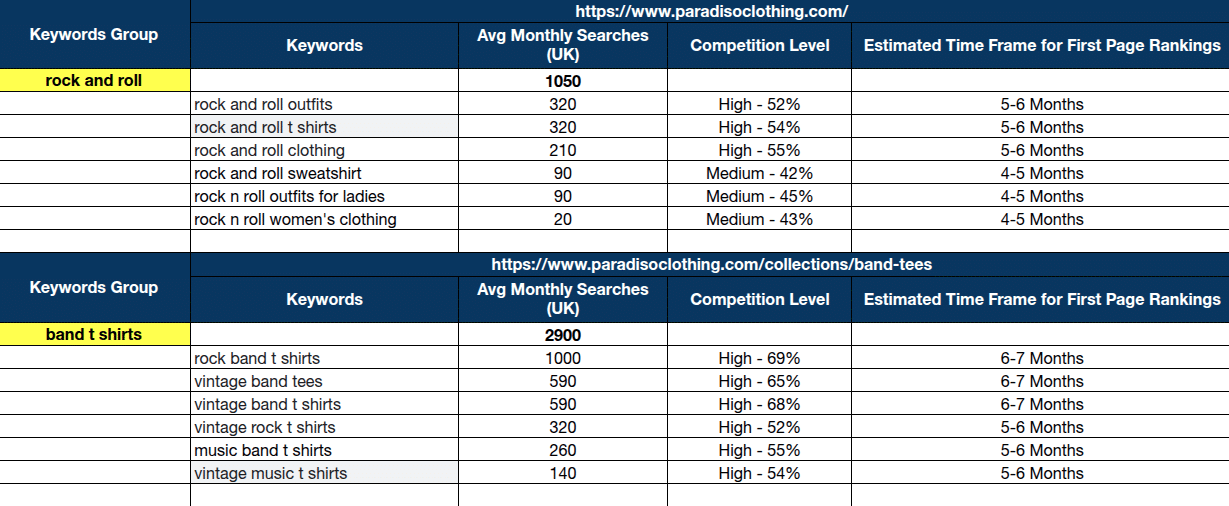
- Identify Relevant Keywords and Subtopics:
Organize all keywords and subtopics that fit within your niche. This will help make sure your content covers all aspects of the topic thoroughly.
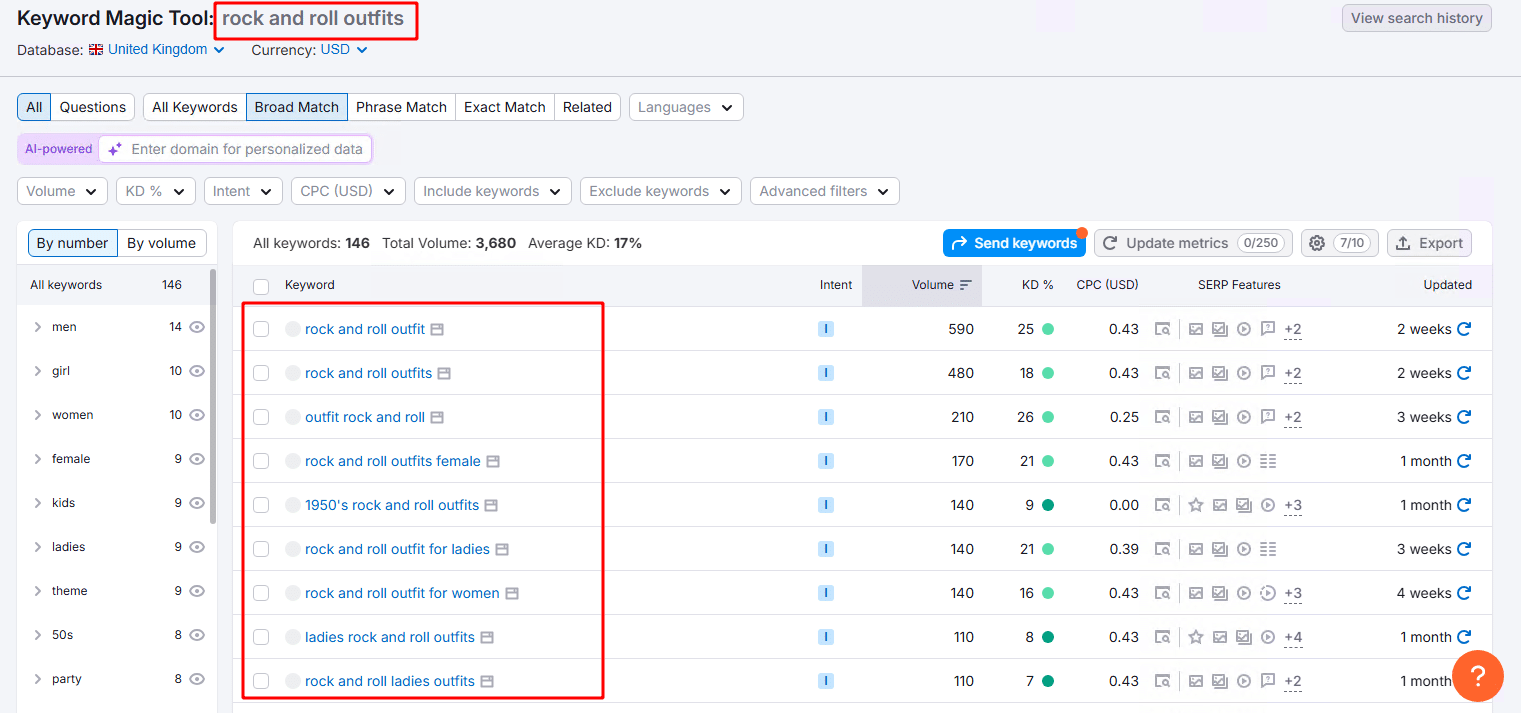
- Use a Mix of Tools:
Leverage tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, Google Keyword Planner, AnswerThePublic, and Google Autocomplete. These tools help you expand your keyword list and uncover related topics and user queries.
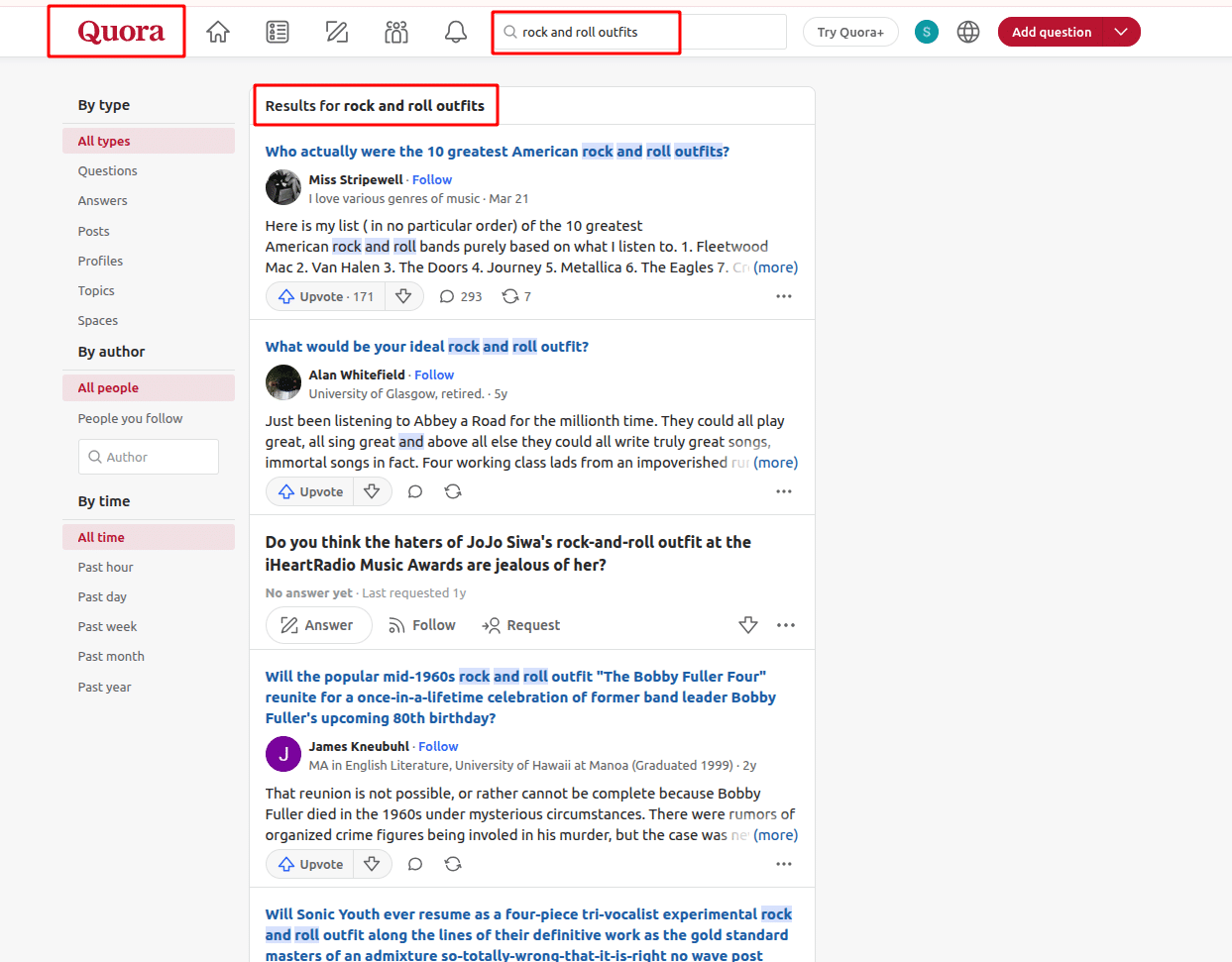
- Analyze communities:
Check forums and community discussions (like Reddit or Quora) to understand how real people talk about issues in your niche. This can reveal additional keywords and phrases you might miss through traditional tools.
- Identify core entities:
Core entities are the main concepts or keywords central to your niche. For example, in “Shopify SEO,” core entities could be “products,” “collections,” and “site speed.” Understanding these entities helps you structure content in a way that aligns with both user needs and search engine expectations, boosting your topical authority.
1.3 Competitor & Gap Analysis
- Evaluate the Competitive Landscape:
This step involves analyzing the top-performing websites in your niche to understand what they’re doing right. By identifying gaps in their content or SEO strategies, you can differentiate your own content and provide additional value, giving you a competitive edge.
- Competitor Set:
Start by identifying the top websites that rank for the keywords you want to target. This helps you understand what works in your niche and what your content needs to compete against. Understanding the competition’s strengths and weaknesses allows you to refine your SEO strategy and find ways to stand out.
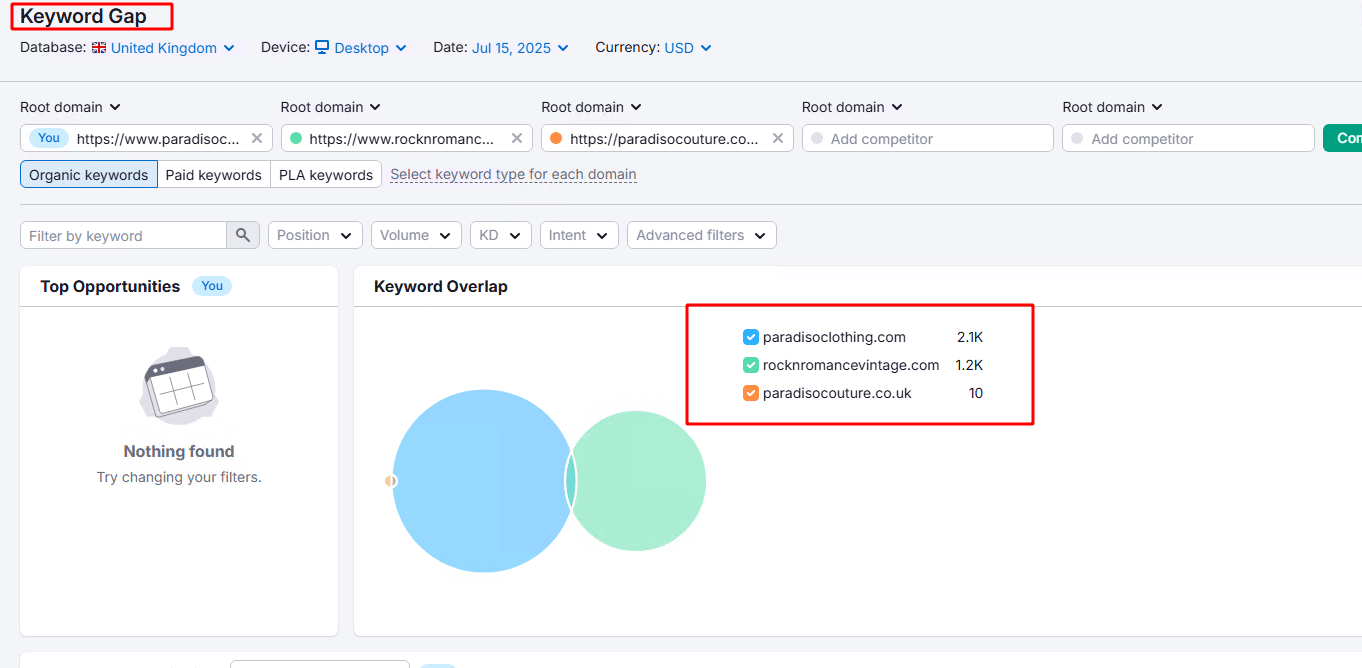
- Content Gap Analysis:
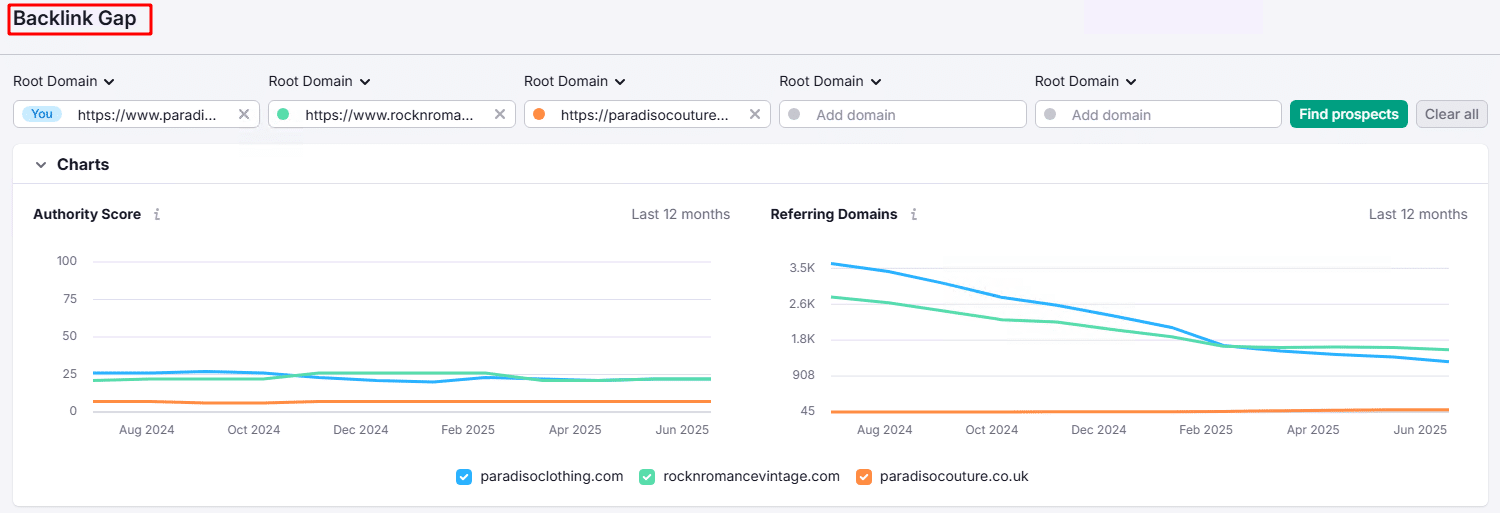
Use tools like Ahrefs’ Content Gap to analyze where your competitors are lacking in content. This will help you identify topics or aspects that your competitors haven’t covered, providing you an opportunity to create content that fills those gaps and adds value that they missed. - Backlink Profiling:
Analyze where your competitors are getting their backlinks from. By profiling their backlinks, you can discover high-quality sources that you can target for your own link-building efforts. This helps you improve your domain authority and stay competitive in search rankings.
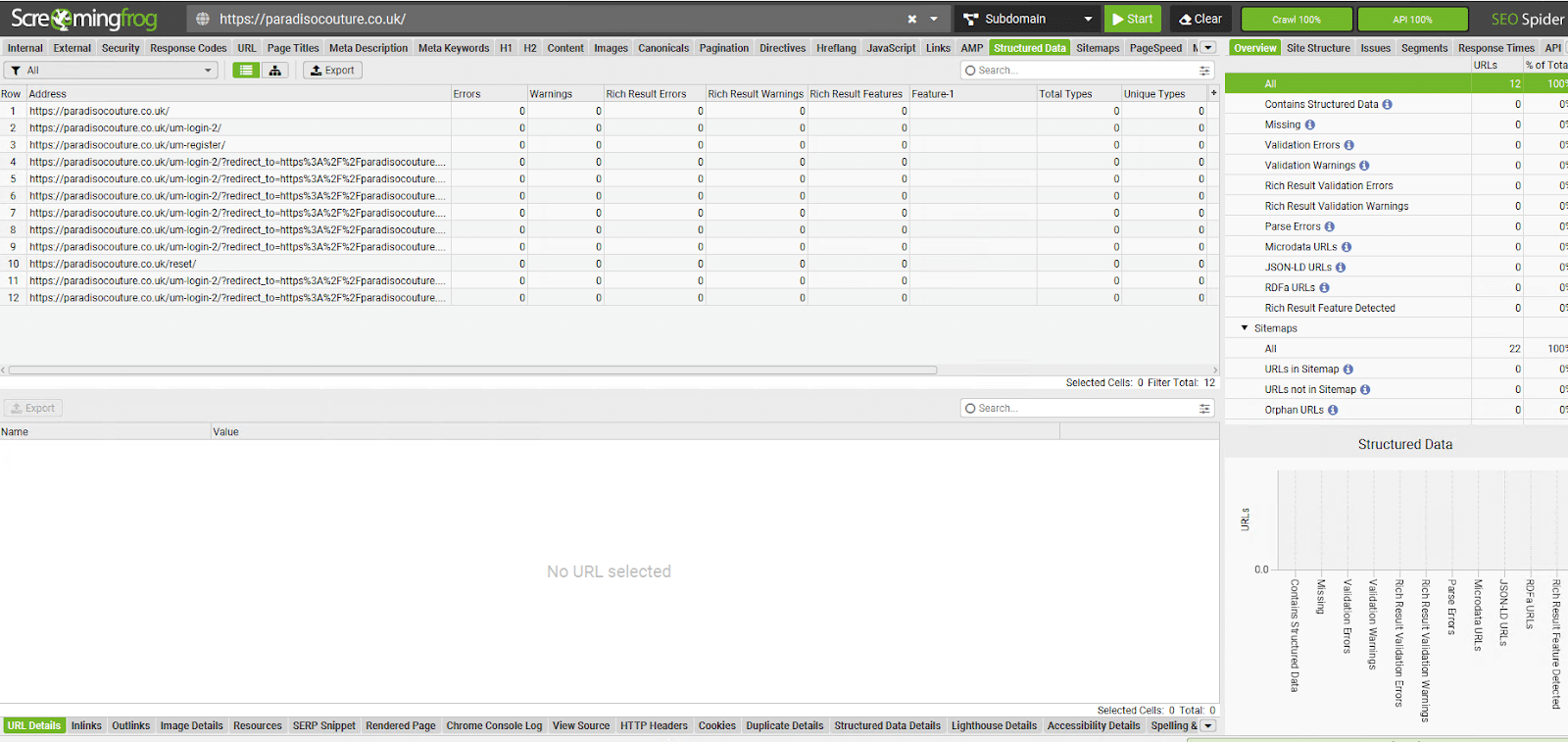
- Technical Audit:
Use tools like Screaming Frog to perform a technical audit of your competitors’ websites. Focus on elements like page speed, mobile responsiveness, and schema markup. Understanding these technical aspects allows you to fine-tune your own site and ensure you’re staying competitive in terms of both user experience and search engine requirements.
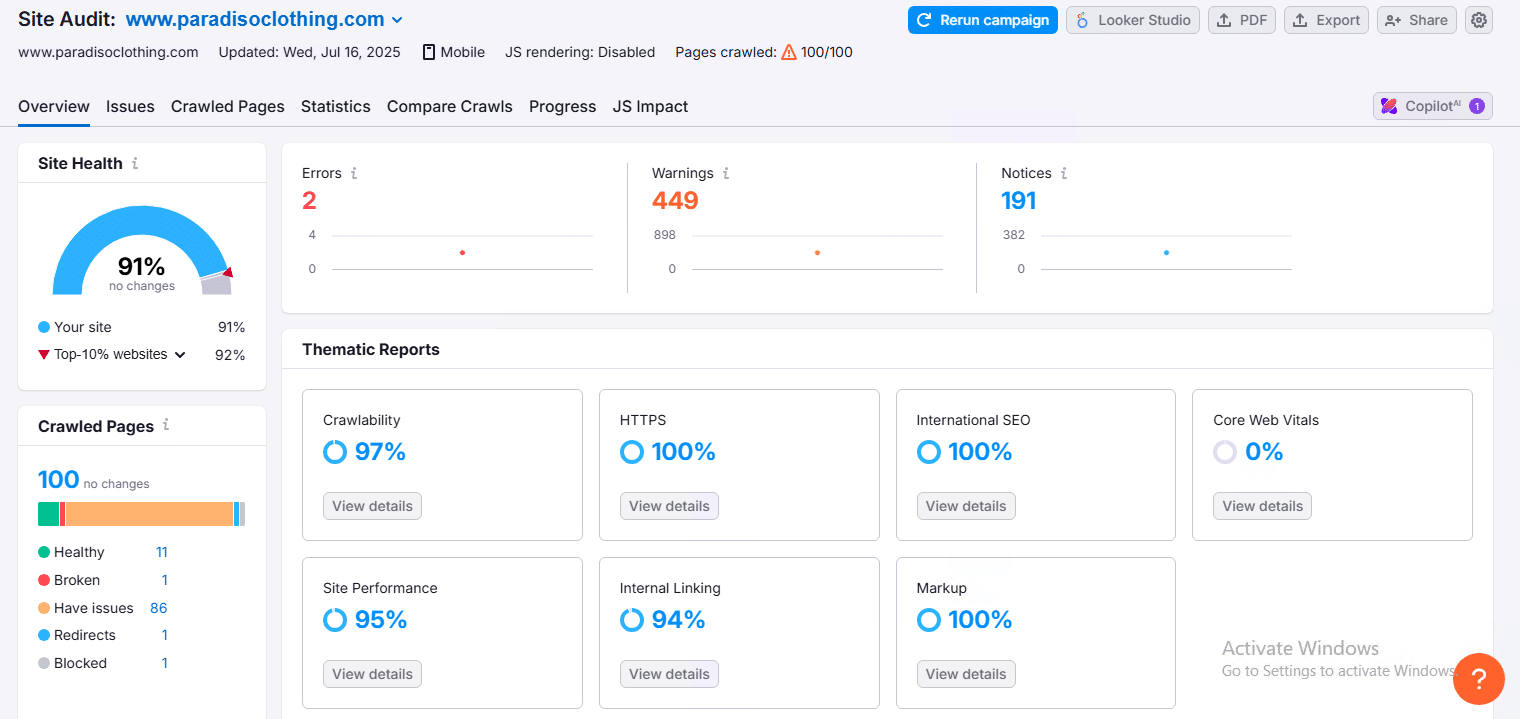
1.4 Maintain Technical Excellence
- Run Regular Site Audits:
Regular audits ensure your site is performing well. Focus on fast load times, mobile-friendliness, and checking for technical errors that could negatively impact SEO and authority.
- Optimize Core Web Vitals:
Core Web Vitals are key user experience metrics Google uses to rank websites. For example, Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) should be under 2.5 seconds for a good user experience and SEO 4. Check these metrics with tools like PageSpeed Insights to ensure you’re meeting Google’s standards.
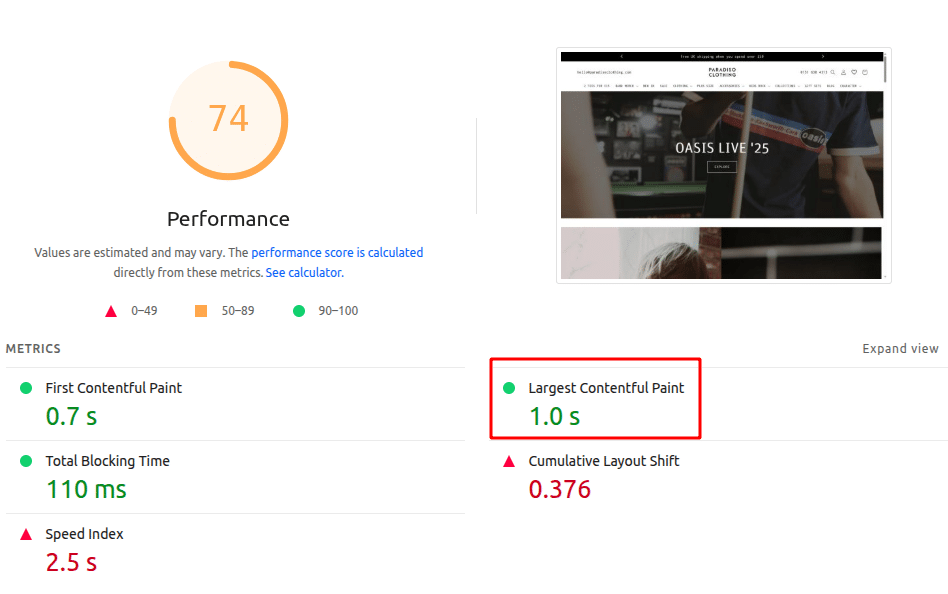
- Ensure Mobile Responsiveness:
With more users browsing on mobile, it’s crucial that your site is mobile-friendly. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to ensure your site adjusts properly across devices and offers a seamless mobile experience.

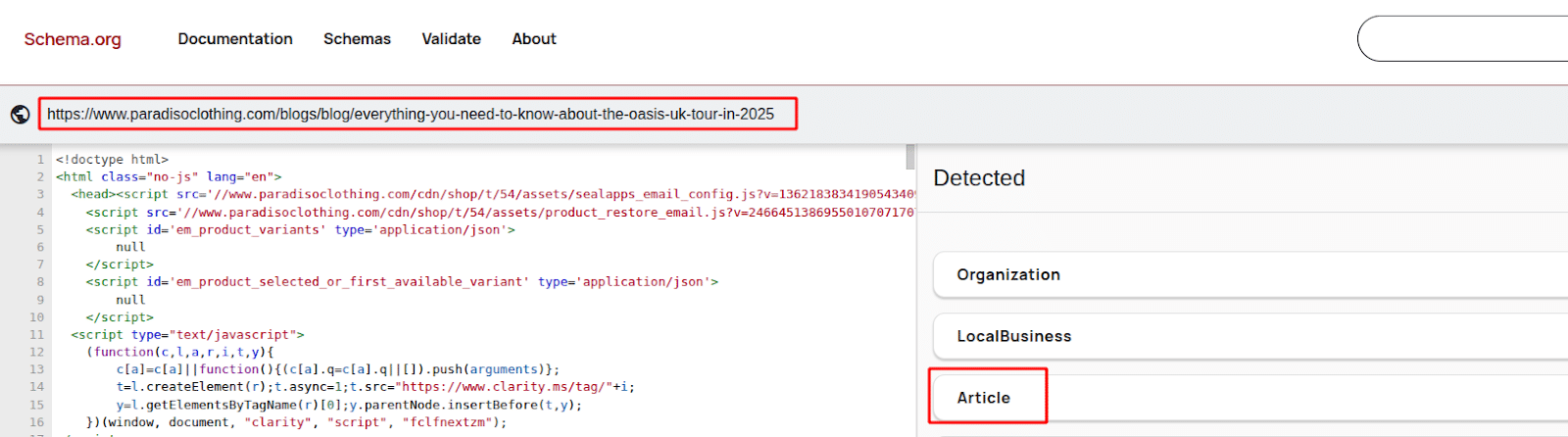
- Add Structured Data (Schema Markup):
Schema Markup is code that helps search engines understand your content better. For example, using Article schema for blog posts tells Google that the content is an article, improving visibility and search results. This helps with features like AI Overviews in search results.
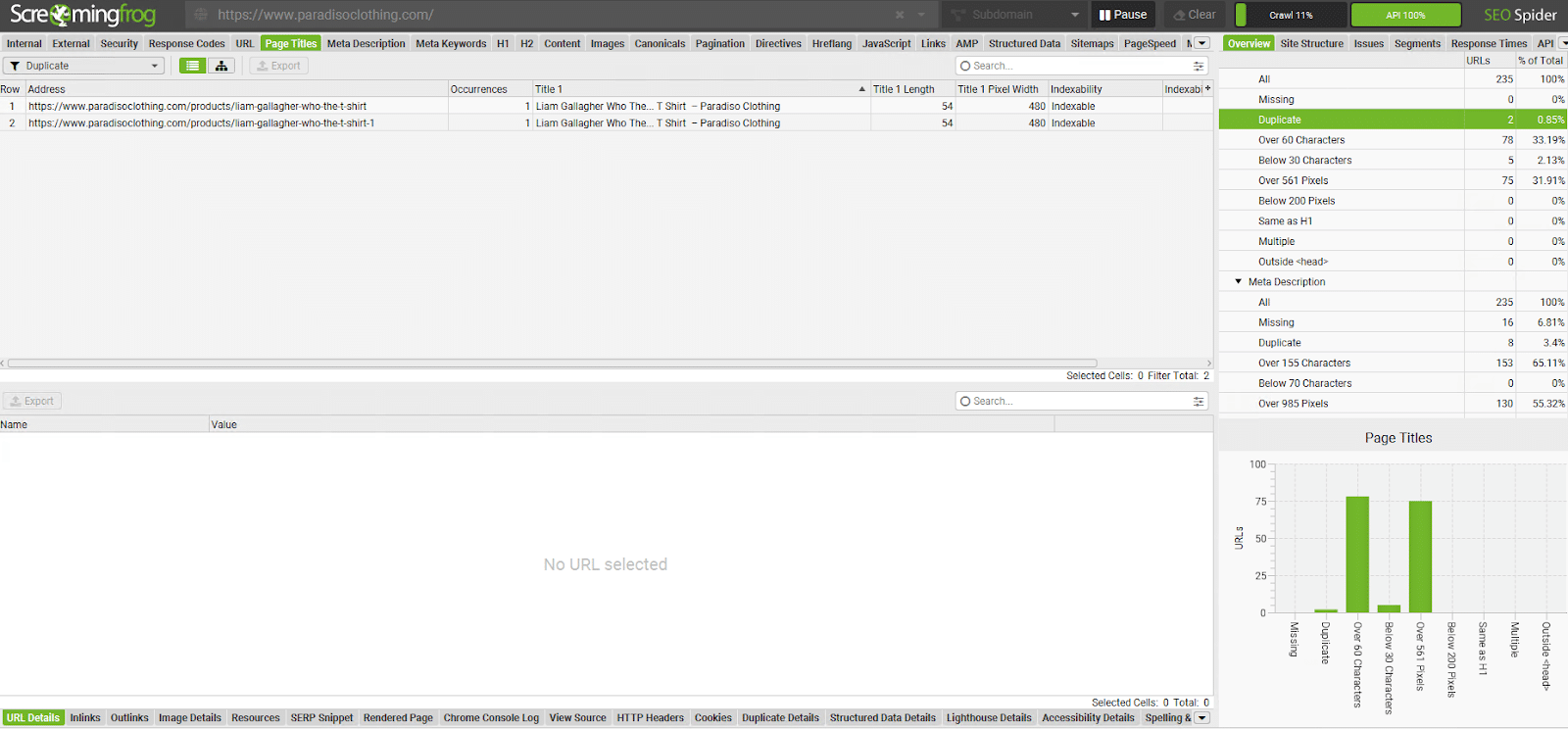
- Use Screaming Frog for Technical SEO:
Tools like Screaming Frog can crawl your website to identify technical issues such as 404 errors, missing metadata, and other problems that affect rankings. Fixing these issues helps your SEO health and site usability.
- Monitor User Signals:
Google considers user signals like dwell time (how long users stay on your site) and click-through rate (CTR) when determining the usefulness of your site. Improving these metrics signals to Google that your site is providing value and boosts your rankings.
2. Content Architecture: (Create Pillar Pages and Topic Clusters)
- Organize Content with Pillar Page and Topic Clusters:
Structure your content to show comprehensive coverage of your topic. The Pillar Page covers the broad aspects of your core topic, and Topic Clusters break down specific subtopics. This interconnected approach signals to Google that your site is an authority on the subject. - Create Your Pillar Page:
The Pillar Page is your primary resource for the broad topic. It should provide an in-depth overview of your subject, like “The Ultimate Shopify SEO Blueprint for 2025.” Focus on depth and value, not just on word count. It should also link out to all relevant cluster pages, acting as the central hub of related content - Develop Topic Clusters:
Topic Clusters are individual articles that dive deeper into specific subtopics mentioned in the Pillar Page. Each cluster should focus on answering specific user queries within a narrow subject. Examples could be:- “A Beginner’s Guide to Shopify Product Page SEO”
- “10 Tips to Speed Up Your Shopify Store”
- “How to Earn Quality Backlinks for Your Shopify Site”
These clusters connect back to the pillar page and provide more detailed insights into areas of interest.
- Internal Linking Plan:
Link each cluster page back to your Pillar Page to establish clear content relationships. Additionally, link related cluster pages to one another where relevant. Use descriptive anchor text (e.g., “learn more about Shopify product page SEO”) to help Google understand the connections between your content. By doing this internal linking, we create a logical structure that reinforces your topic’s authority and relevance.

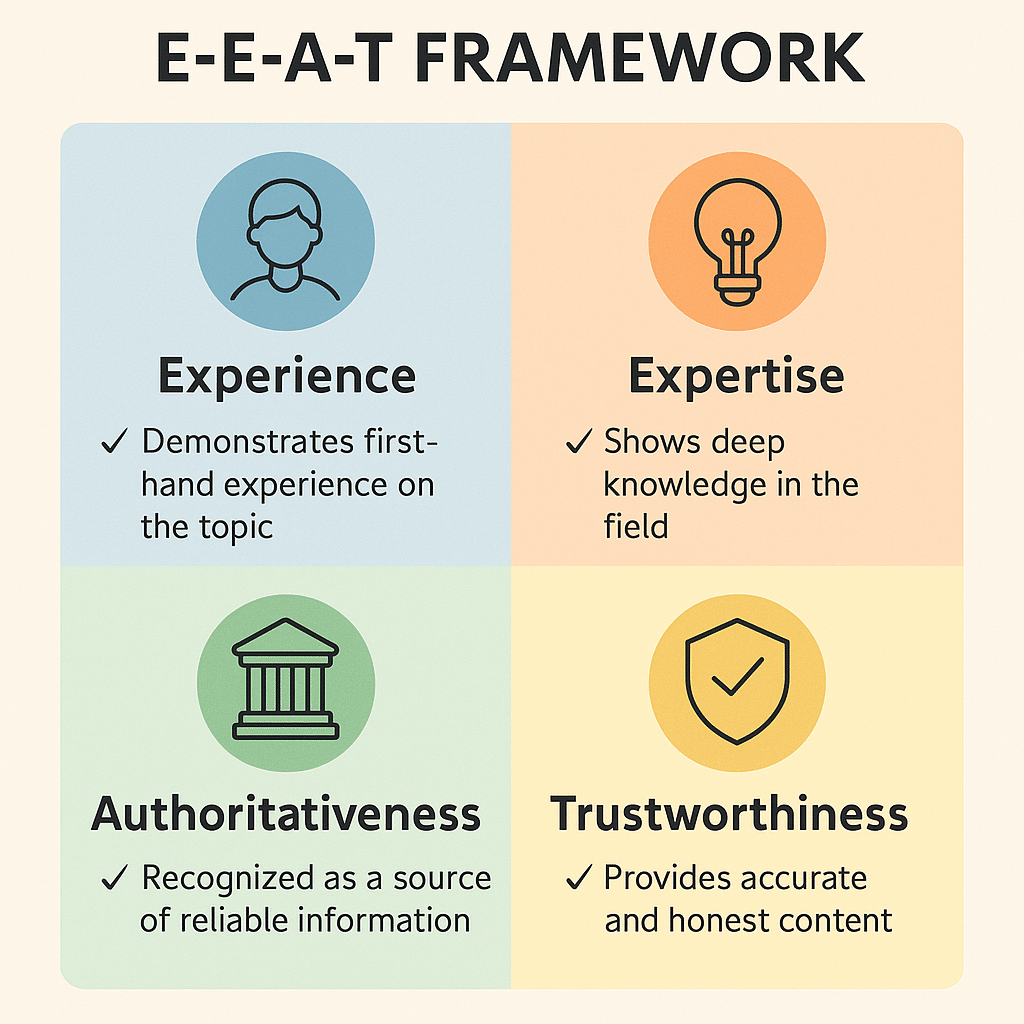
3. Demonstrate Expertise with Consistent, High-Quality Content (Content Creation & E-E-A-T)
- Google Values High-Quality, Detailed Content:
Regularly publishing detailed articles that answer real questions, solve user problems, and provide in-depth guidance is essential for SEO success. This demonstrates your expertise and directly ties into E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), which Google uses to assess the quality of content.
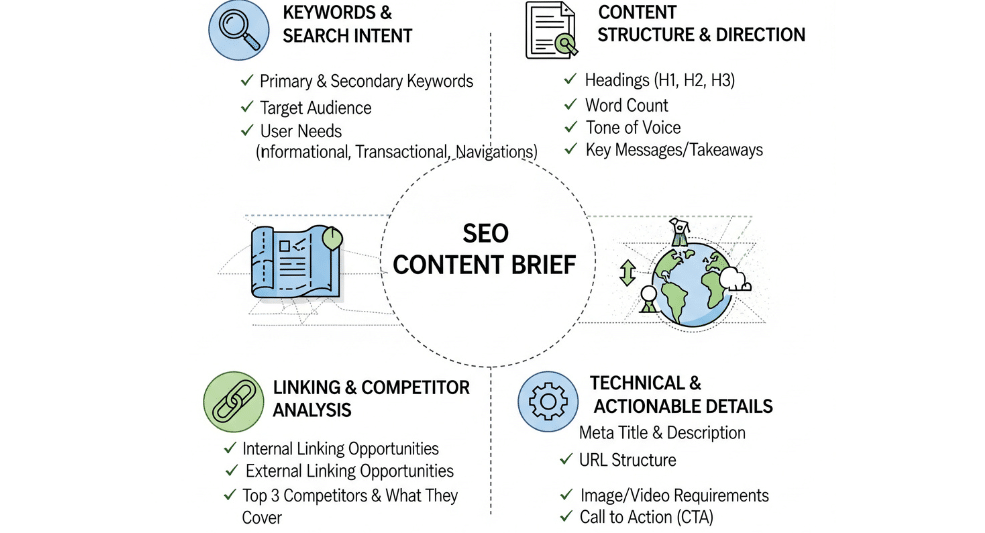
- Create Detailed Content Briefs:
Before writing, create a content brief to ensure your article is well-organized and aligned with SEO goals. Your content brief should include:- Primary Keyword: The main keyword or phrase you’re targeting for SEO.
- User Intent: The reason behind the search query (informational, transactional, etc.).
- Target Persona: Who you’re writing for – a specific audience segment.
- Internal Links: Where you will link to relevant content on your site.
- E-E-A-T Elements: Plan for using multimedia, CTAs, and cross-links to enhance trustworthiness and the user experience.
- Prioritize Depth and Unique Value:
Ensure your content is thorough and covers all important aspects of the topic. Provide unique insights or perspectives that aren’t available elsewhere, such as:
- Case studies
- Data-backed research
- Personal experiences
Offering these types of content adds value and sets you apart from competitors.
- Incorporate key elements of E-E-A-T into your content:
- Experience: Share first-hand stories or lessons learned from real-world experiences. Using “I” or “we” helps humanize your content and makes it feel less generic.
- Expertise: Include author bios with credentials and social links to demonstrate authority. Reference reputable sources and cite data to back up your claims.
Credit: James Clear
-
- Authoritativeness:
Reference industry studies, official documentation, or leaders to back your content with authoritative sources. - Trustworthiness:
Ensure your site has a clear editorial policy, easy-to-find contact information, and a secure HTTPS connection, all of which build trust with both users and Google.
- Authoritativeness:
- Optimize for Readability and Engagement:
Good content is not only about information but also how it is presented. Use tools like Hemingway App or Grammarly to ensure clarity. Break up long paragraphs with:- Short, digestible paragraphs
- Headings and subheadings
- Bullet points and block quotes
- Use rich media like annotated screenshots, charts, GIFs, and videos to engage users and explain complex ideas in an accessible way.
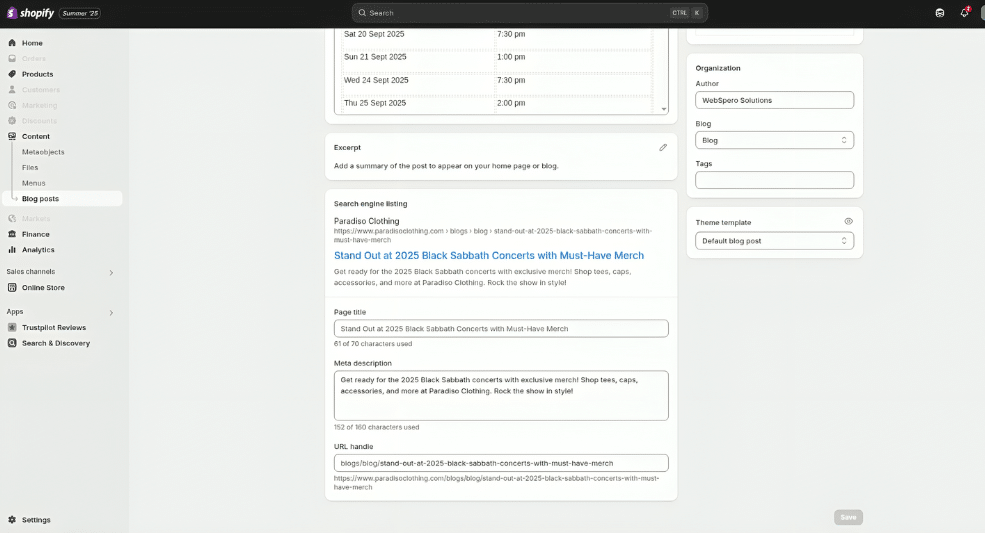
- On-Page Polish:
The technical aspects matter too. Ensure your content is optimized for both users and search engines by:- Title tags, meta descriptions, and URL slugs that include the primary keyword.
- Solid internal linking to other relevant content on your site.
- Valid Schema.org markup to help search engines better understand your content.
- User Experience (UX):
UX is a crucial factor in how Google evaluates your site. Conduct regular UX audits using tools like Hotjar and Google Analytics 4 (GA4) to identify where users are struggling. Use this data to improve navigation, simplify tasks, and enhance overall user satisfaction on your site.
To further optimize for AI Overviews use:
|
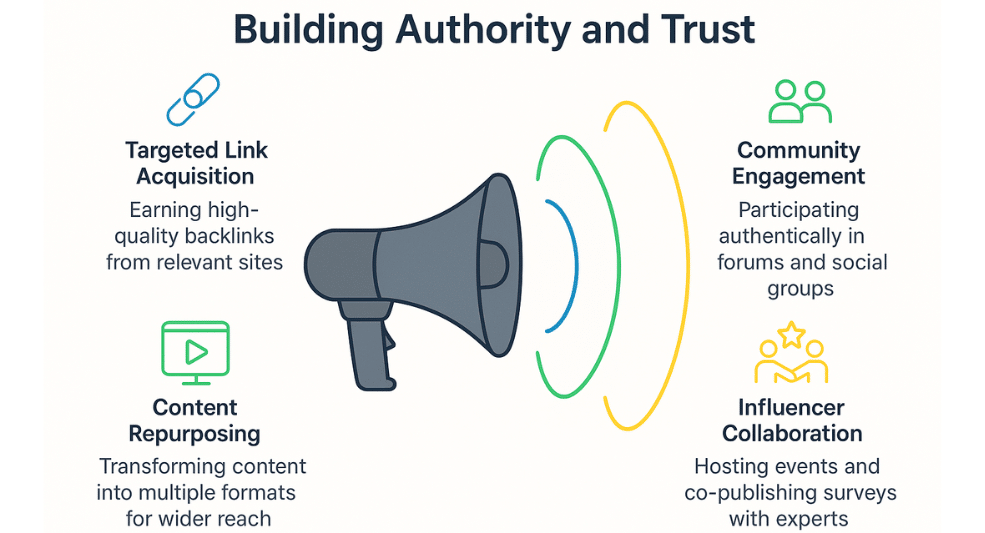
4. Promotion & External Validation (Earn Backlinks)
Amazing content is useless if no one sees it. You need to promote your content and earn backlinks, which act as third-party votes of confidence.
When authoritative sites in your niche link to your content, it’s like getting a recommendation from an expert in the field. These backlinks signal that your content is trustworthy and valuable to users.
- Focus on Quality Over Quantity:
It’s better to have a few high-quality, relevant backlinks than many low-quality ones. A link from a reputable site within your niche holds more SEO value than links from unrelated or low-authority sites.
- Personalized Outreach:
Reach out to websites, blogs, or businesses with a similar audience (but not direct competitors). Personalize your outreach to increase response rates and improve your chances of earning a valuable backlink.
- Strategic Guest Posting:
Write content for other websites in your industry or niche (guest posts) to acquire backlinks while showcasing your expertise. These backlinks will help build your site’s authority.
- Digital PR:
Pitch original research, data, or expert commentary to journalists using platforms like HARO (Help a Reporter Out), Featured.com to secure backlinks from high-authority media sites.
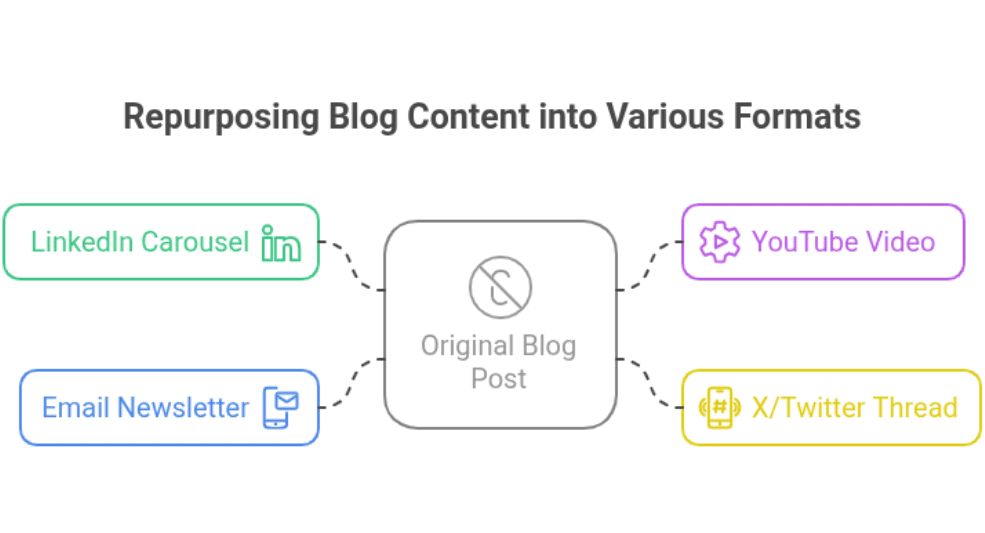
- Build a Content Repurposing Engine:
Maximise Content Reach by taking a single piece of content and repurposing it into various formats, such assuch as:- Blog posts → Videos
- Social media posts → Infographics
- Article → A 5-slide LinkedIn carousel with key stats
- How-to guide → A 3-minute YouTube tutorial video
- Tips list → A 7-tweet X/Twitter thread of “quick tips”
- In-depth post → A “Tip of the Week” in your email newsletter
- Webinar → A summary blog post with key takeaways
- Case study → A series of Instagram stories or posts highlighting key points
This helps you reach a wider audience across different platforms and engage users more effectively.
- Build Trust Through Community & Influencer Engagement
Become an active, helpful member of your niche by:- Participating Authentically:
In forums or social groups (e.g., Reddit or LinkedIn), focus on contributing real value. Only share your content when it’s genuinely helpful and relevant, as spamming links can harm your credibility. - Hosting Events:
Running events like monthly AMAs or webinars builds trust with your audience. It also positions you as an authority. Hosting events with industry experts strengthens your reputation as a trusted source of information. - Co-publishing Industry Surveys:
Surveys give valuable insights into your niche. By co-publishing surveys or sharing trend reports, you establish yourself as a thought leader. These can attract backlinks from sites referencing your data or insights. - Becoming Community Leader:
As your authority grows, consider taking on leadership roles (e.g., becoming a moderator) in relevant communities. This strengthens your reputation, boosts visibility, and gives you opportunities to share your content with a larger audience.
- Participating Authentically:
5. Measure, Optimize, & Scale (Ongoing Systems)
Topical authority isn’t a “set it and forget it” project. It requires a continuous loop of monitoring, refining, and expanding.
How to Implement It:
5.1 Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Track Success:
KPIs are essential metrics for measuring the effectiveness of your strategy. For topical authority, key KPIs to track include:
- Organic traffic: How much traffic your site is getting from search engines.
- Keyword rankings: Positions of your target keywords in search results.
- Engagement metrics: Metrics like time on page, bounce rate, and user interactions.
- Conversion rates: How well your content drives conversions (e.g., sign-ups, purchases).
- Example Benchmarks:
- Advanced Tracking:
- Micro-conversions: Track smaller actions like CTA clicks or lead magnet downloads.
- Brand mentions: Set up alerts using tools like Brandwatch or Mention to track your brand’s visibility.
- Content decay: A >25% traffic drop signals content that may need refreshing or updating.
5.2 Implement a Content Refresh Framework:
- Keep Content Relevant:
Regularly update your content to ensure it stays valuable for both users and search engines, and continues to rank well over time. - Trigger for Refresh:
- Instead of refreshing on a set schedule, monitor your content’s performance. Key signals include:
->20-30% traffic drop or
->A 5-position drop in keyword rankings. These are indicators that the content may be losing its relevance or authority.
- Instead of refreshing on a set schedule, monitor your content’s performance. Key signals include:
- Refresh Actions:
- Refresh Actions:
- Update statistics and replace outdated data.
- Fix broken links and replace outdated screenshots.
- Re-optimize titles and meta descriptions to improve Click-Through Rates (CTR).
- Add fresh, valuable information to ensure your content stays comprehensive.
- Advanced Refinements:
- Shifting search intents: Use tools like Surfer SEO to analyze changes in user intent around your topic and adjust accordingly.
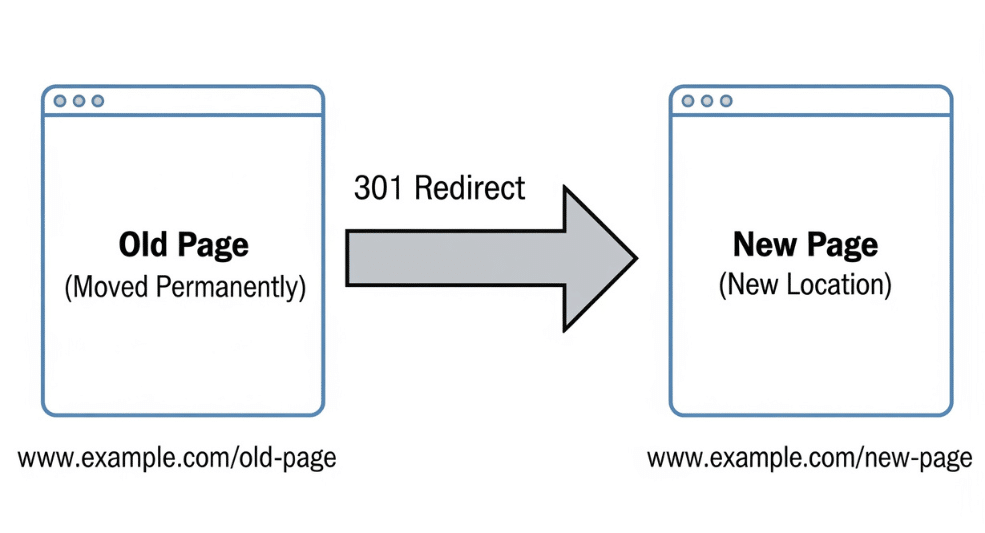
- Consolidate weak articles: If some articles aren’t performing well, use 301 redirects to consolidate them and pass authority to stronger pages.
-
- Schema upgrades:
Add structured data, such as FAQPage or HowTo, to improve search engine visibility and user engagement.
- Schema upgrades:
5.3 Expand Strategically:
- Use Data from Top-Performing Content:
- As you gain authority in your niche, look at your best-performing content to identify potential opportunities for new content clusters.
- Focus on expanding where there’s strong search demand and align this with user interests.
- As you gain authority in your niche, look at your best-performing content to identify potential opportunities for new content clusters.
- Identify New Clusters:
- Analyze rankings, backlinks, and engagement metrics to determine which topics have the potential to drive more traffic.
- Build new content clusters based on these insights, expanding your topical authority.
- Diversify Traffic:
- Once you have a solid organic SEO foundation, use paid advertising (e.g., LinkedIn or Reddit ads) to expand your reach.
- Paid traffic can introduce your content to a wider audience, boosting your overall visibility and audience engagement.
| Building topical authority is a deliberate, ongoing process that combines deep content, smart structure, and genuine engagement.
By following this blueprint, you move beyond simply ranking for keywords and begin building a durable digital asset that establishes your brand as the definitive leader in your niche. |
Resources & Tools
Key Terms (Glossary)
- AI Overviews: AI-generated summaries at the top of Google searches, aiming to answer queries directly.
- Backlinks: Links from other websites to your content. Backlinks from trusted, authoritative sites act as “votes” that suggest your content is valuable.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of visitors who leave your website after viewing only one page, indicating low engagement.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of users who click on a specific link after viewing it.
- Content Brief: A document that outlines the key components of an article before it’s written, including primary keyword, user intent, target persona, internal links, and E-E-A-T elements.
- Content Decay: A significant drop in an article’s traffic (e.g., >25%) or keyword rankings (>5 positions), signalling a need for an update.
- Content Gap Analysis: Analyzing the top-performing sites in your niche to identify content that your competitors are missing, creating an opportunity to add value.
- Content Repurposing: Taking a single piece of content and transforming it into multiple formats (e.g., a blog post into a video, social media posts, infographics) to reach a wider audience.
- Core Entities: The main concepts or keywords central to your niche. Understanding how these entities relate helps structure content for both users and search engines.
- Core Web Vitals: Google’s set of user-centric metrics (like Largest Contentful Paint) measuring the quality of a website’s user experience.
- CTAs (Calls-to-Action): Prompts (e.g., buttons, text links) designed to encourage users to take a specific action, like signing up or making a purchase.
- Digital PR: Pitching original research, data, or expert commentary to journalists using platforms like HARO (Help a Reporter Out) to earn media mentions and backlinks.
- Dwell Time: How long users stay on your site after clicking a search result, signaling engagement to Google.
- E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness): Google’s criteria for evaluating the quality and reliability of content, influencing trust and rankings.
- Entity-Rich Content: Content that incorporates specific entities to help Google understand its context, improving its chances of being highlighted in AI-driven search results.
- Guest Posting (Strategic): Writing content for other websites in your industry or niche to acquire backlinks while showcasing your expertise.
- KPIs (Key Performance Indicators): Metrics that help you track the success of your strategy, such as organic traffic, keyword rankings, engagement, and conversion rates.
- Keyword Mapping: The process of identifying and organizing all relevant keywords and subtopics that define your chosen niche, ensuring comprehensive content coverage.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures how quickly the largest visible content on a page loads. A score under 2.5 seconds is ideal for good user experience and SEO.
- Moat: A competitive advantage that protects your business from competition, making it difficult for rivals or AI to replicate your success.
- Niche: A specific segment of a larger market or topic. For example, within the broader category of “SEO,” a niche might be “Shopify SEO” or “content marketing for e-commerce.”
- Personalized Outreach: Reaching out to other websites, blogs, or businesses with tailored messages to acquire backlinks.
- Personas: Fictional representations of different types of users who might visit your site, used to tailor content to their specific needs and preferences.
- Pillar Page: A broad, comprehensive resource that covers the main aspects of your core topic, linking out to related cluster pages.
- ROI (Return on Investment): A performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency or profitability of an investment.
- Technical Audit: Analyzing the technical aspects of a website (e.g., page speed, mobile responsiveness, schema markup) to identify and fix issues that can affect rankings.
- Topic Cluster: Focused, in-depth articles related to specific subtopics mentioned in your pillar page, answering specific user queries.
- Topical Authority: The recognition by search engines and your audience that your website is the most comprehensive and trustworthy source of information on a specific subject.
- User Engagement: Metrics (like time spent on page, clicks to other pages, return visits) that signal to Google whether your content is useful.
- User Intent: The purpose behind a user’s search (e.g., informational, transactional, navigational).
- User Experience (UX): How users interact with and feel about a website, encompassing ease of use, accessibility, and satisfaction.
- Zero-Click SEO: The phenomenon where search engines provide direct answers to users right in the search results, without the need for clicks to a website.
Recommended Tools
| Purpose | Tools |
| Keyword Research | Semrush, Ahrefs, Google Trends, SurferSEO, Keyword Insights, Frase, AlsoAsked, Ubersuggest |
| Content Optimization | Surfer SEO, Grammarly, Hemingway App |
| Technical SEO | Screaming Frog, Google PageSpeed Insights, Google Mobile-Friendly Test, Sitebulb, Google Search Console, Bing Webmaster Tools, Schema.org Validator |
| Backlinks | HARO, BuzzSumo, Ahrefs, Semrush, Featured.com |
| User Experience (UX) | Hotjar, Google Analytics 4 (GA4), Microsoft Clarity |
| Brand Monitoring | Brandwatch, Mention |
Citations
1. Search Engine Land. (May 18, 2021). Google previews MUM, its new tech that’s 1,000× more powerful than BERT. Retrieved from https://searchengineland.com/google-previews-mum-its-new-tech-thats-1000x-more-powerful-than-bert-348707?utm_source=chatgpt.com
2. Search Engine Land. (June 2, 2025). What is AI SEO?. Retrieved from https://searchengineland.com/guide/what-is-ai-seo
3. Ahrefs. Zero-Click SEO: Everything You Need to Know About Zero-Click Search Results. Retrieved from https://ahrefs.com/blog/zero-click-search/
4. Google. (March 20, 2025). Largest Contentful Paint (LCP). Retrieved from https://web.dev/articles/lcp
5. Databox. (2025). 27 Blogging Statistics That Will Shape Your Content in 2025. Retrieved from https://databox.com/blogging-statistics
6. CXL. Benchmark study on bounce rates. Retrieved from https://cxl.com/guides/bounce-rate/benchmarks/
